At SafeSec Day 2025, organised jointly by TÜV Akademie Austria and msg Plaut Austria, Markus Benedikt from LieberLieber held a workshop explaining the integration of safety and security standards in model versioning with LemonTree, using practical examples.
In his workshop, Markus Benedikt emphasised the major advantages of model-based systems engineering (MBSE), which range from reducing the complexity of requirements to the verifiable integration of safety and security standards. “MBSE makes it very easy to reduce physical and digital risks in products and systems. To make the principles to be observed clear and easy to understand, I chose the practical example of “developing a smart water boiler,” explains Benedikt. Let’s assume that a company is developing a smart water boiler with IoT functions that can be controlled via an app and displays the water level, temperature and energy consumption. During development, all relevant safety and security standards must of course be taken into account:
- Safety: Prevention of physical hazards such as overheating, electric shock or improper use
- Security: Protection of user data and prevention of unauthorised access to the kettle

Markus Benedikt spoke at SafeSec Day 2025 about model versioning with LemonTree and the integration of safety and security standards.
Creation of a structural model
In a first step, the participants developed a common understanding of the components and their relationships in order to specifically assign safety and security requirements. The main components of the water boiler were defined on a whiteboard and the data and energy flows were presented. Each team member described the function of a specific component, and the safety risks were discussed together. ‘In this step, the group developed a complete and visualised structural model of the kettle with all the main components and their connections as a basis for all further activities,’ explains Benedikt.
From requirements to risk assessment
Based on the jointly created structural model, the next step was to assign the safety and security requirements to the components in a practical manner. This step was carried out using labelled cards and interactive discussion. The group had thus supplemented the model with specific requirements and could now turn its attention to risk assessment. ‘In this step, which is extremely important for the process, potential risks to safety and security are to be identified and appropriate countermeasures developed,’ says Benedikt. The participants’ imagination is called upon when developing corresponding scenarios and possible preventive measures. The result of the lively discussions is ultimately an overview that contains risks and countermeasures for each component.
Emergency plan and checklist
The workshop made it clear that it is particularly important to be prepared for various scenarios, both preventively and reactively. ‘It is especially good when dangers can be identified and prevented in advance. However, since this is not always possible, clear instructions for action must also be established so that they can be implemented quickly in the event of an emergency,’ says Benedikt. This results in both an emergency plan and a checklist for safety and security. ‘The participants in my workshop were very involved in our exercises and were impressed by the practical focus of the individual steps. With this preparation, they can now, with the support of LemonTree, take practical steps in their companies to translate the often very theoretical concepts of safety and security into practical solutions.’
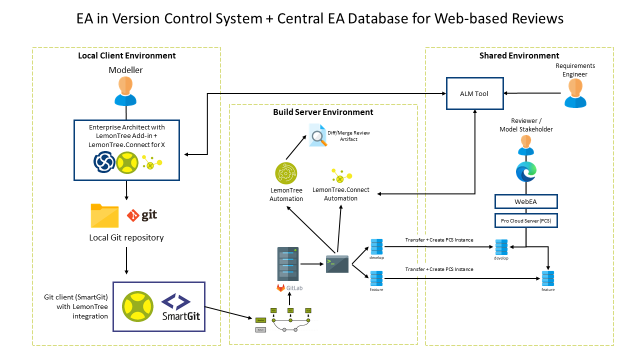
This integrated setup demonstrates how Enterprise Architect (EA), combined with LemonTree and version control systems like Git, enables a consistent and traceable model management workflow. By automating synchronization through LemonTree.Connect and LemonTree.Automation, and centralizing collaboration with Pro Cloud Server and WebEA, teams can ensure seamless versioning, efficient reviews, and clear traceability across distributed environments. This approach supports model integrity, accelerates feedback cycles, and enhances overall project transparency and collaboration.
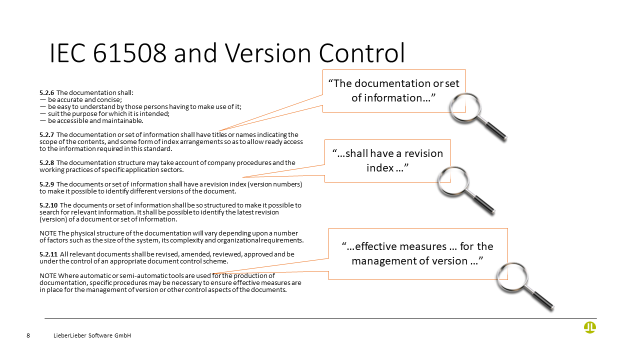
Managing the resulting model versions is particularly important in complex MBSE scenarios. LieberLieber recommends combining Git with Lemontree, which produces particularly good results.

